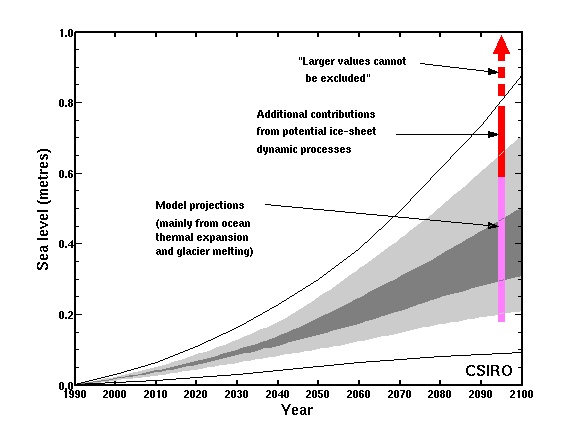
Figures marked "CSIRO", are copyright CSIRO, but please feel free to use them, conditional on the figures not being altered, and their source being acknowledged, and with a link to this site where possible. All other figures are copyright. Please do not copy without the owner's permission.
|
About the projectIntroductionOur sea level research at CSIRO's Oceans and Atmosphere Flagship and the Antarctic Climate and Ecosystems Cooperative Research Centre (ACE CRC) is focused on understanding recent (20th century and early 21st century) sea level change as a basis for improving projections of future sea level rise. We use data from tide gauges and satellite altimeters to determine past changes in global mean and regional sea level. We also attempt to understand the reasons for past changes and and use model results for improved projections of future sea level rise. Our sea level recordSome of our work is:
Project objectivesOur work is focused on determining and understanding 20th century (and early 21st century) sea level rise as a basis for improving projections of 21st century sea level rise. Our specific objectives are:
|
|
Website owner: Benoit Legresy | Last modified 6/01/15
|
![]()